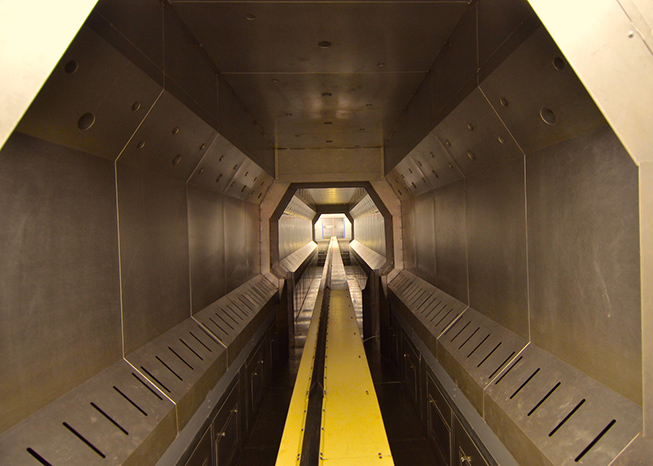
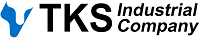Industrial Oven
TKS manufactures custom industrial ovens for paint cure, parts curing, thermal treatment, and more.
We offer batch ovens, continuous ovens, cure ovens, bake ovens, and dry-off ovens.
Turn-key Industrial Ovens
TKS offers design, build, install, and start-up services for custom industrial oven systems. We have built industrial ovens of the following types: drying ovens, batch ovens, cure ovens, paint ovens, and more.
TKS has designed and built industrial ovens for major Fortune 500 manufacturers, including:
- Automotive OEMs:
- Honda, Nissan, Toyota, Kia, Subaru, Mazda, etc.
- Automotive Tier-1 Parts Suppliers:
- Heartland, Chiyoda, Eakas, Kosei, TOA, etc.
- Aerospace:
- Boeing
- Heavy Trucking / Semi trucks:
- Hino Motors, several US-based Semi truck manufacturers, etc.
- Motorcycle:
- Harley Davidson
- ATV/UTV/4x4/SxS - recreational vehicles:
- Honda, Polaris, Suzuki, Kawasaki, etc.
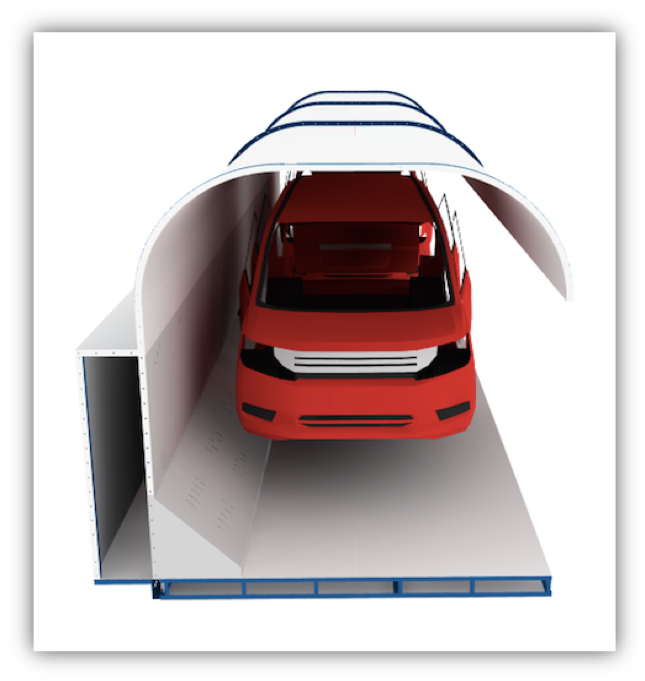
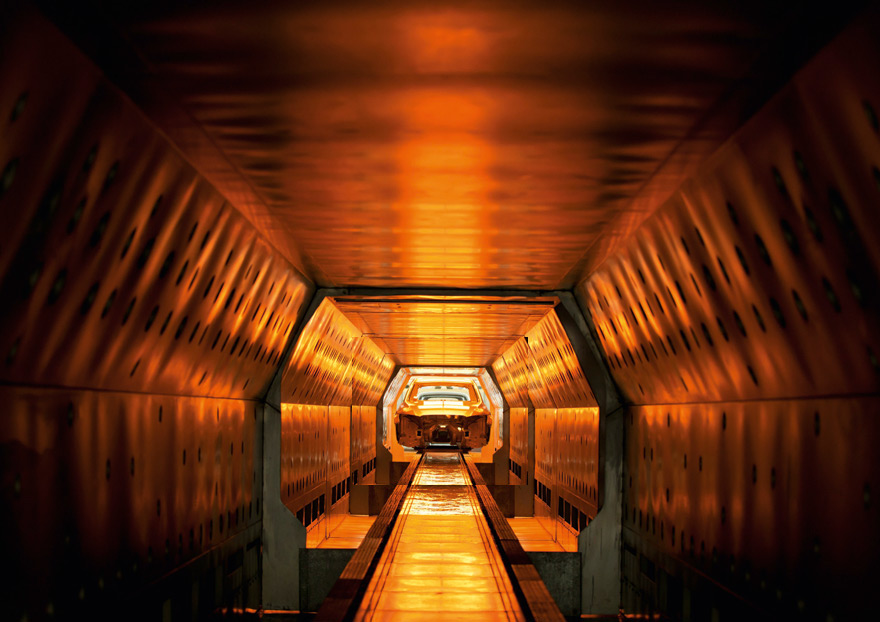
TKS Industrial's long oven design (non-batch oven) consists of three main parts.
- The oven is typically split up into two or more sections. The first section is the heat up zone. TKS offers three different types of heat up for an oven:
- Infrared (IR) lamps, no forced air
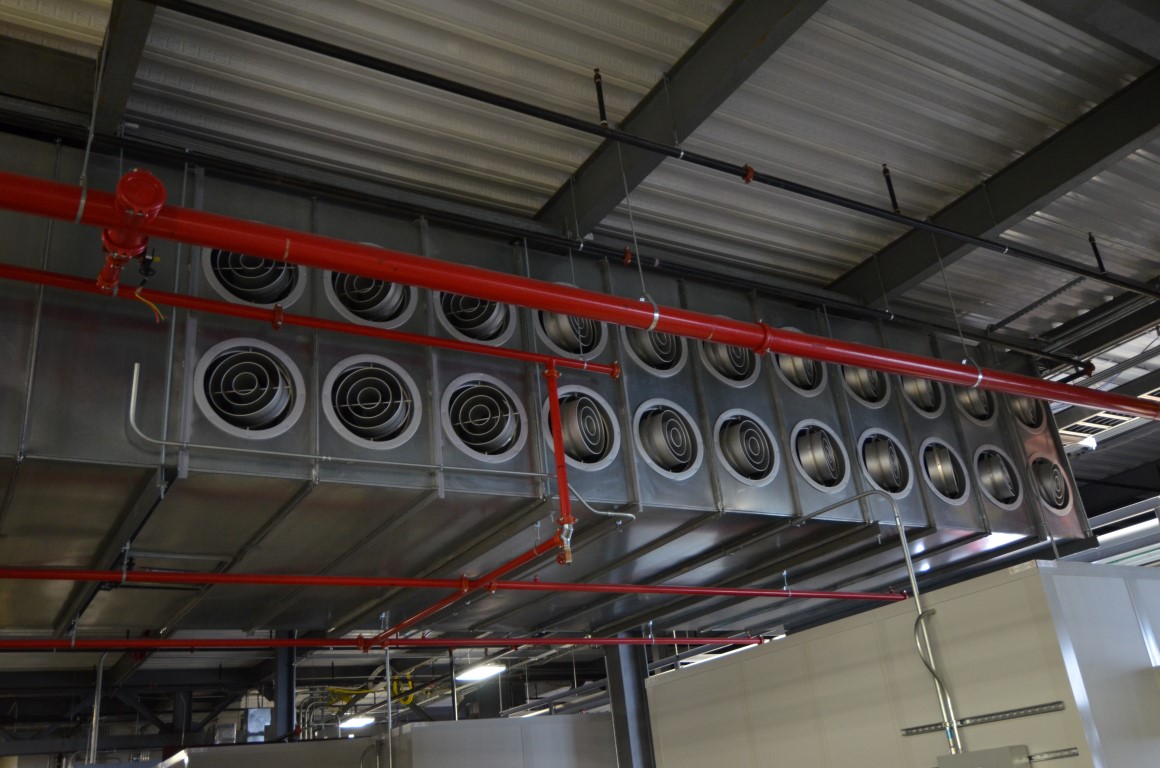
- Convection flow heated with forced hot air
- Radiant heating, no forced air
- The next section of the oven is the hold zone, where the actual paint cure takes place. The hold zone for metal parts is typically heated via convection / forced hot air style. For plastic parts, a lower air temp is used as to not melt or soften the plastic part itself. The hold zone for curing most paints is 18-20 minutes at the cure temperature. Each paint supplier will dictate the "cure window" or the time/temp window for proper paint cure. Burner sizing is not so critical here because there should be no heat load, simply maintaining temperature.
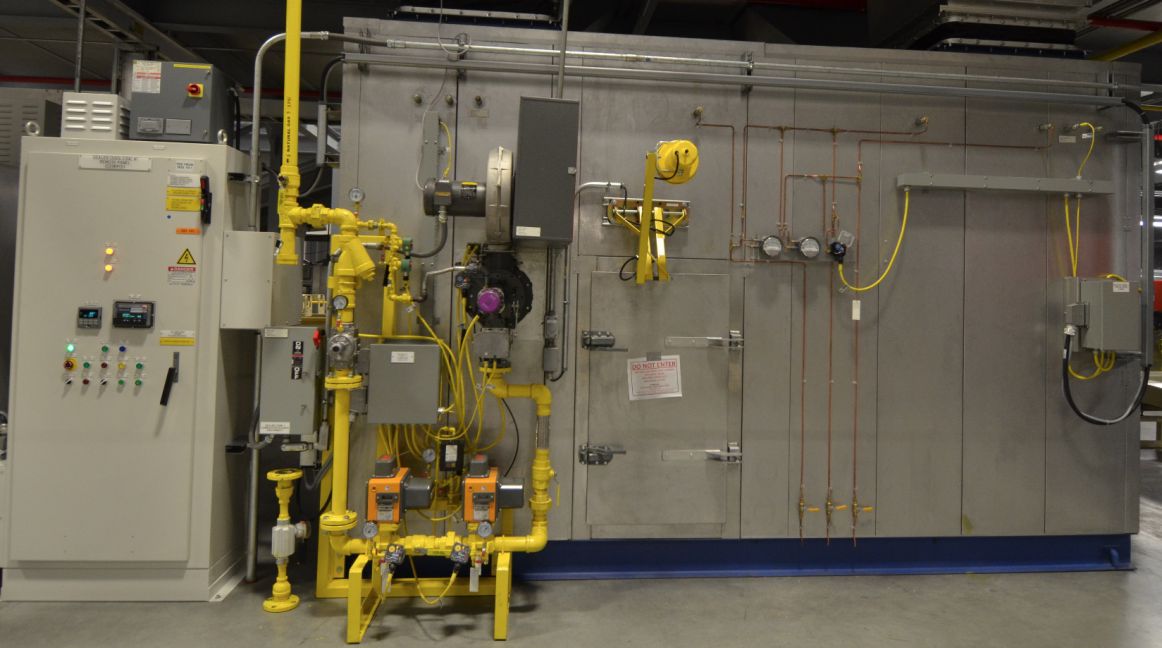
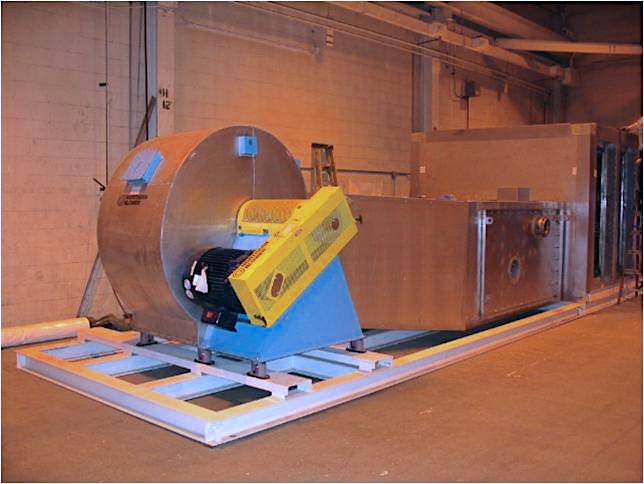
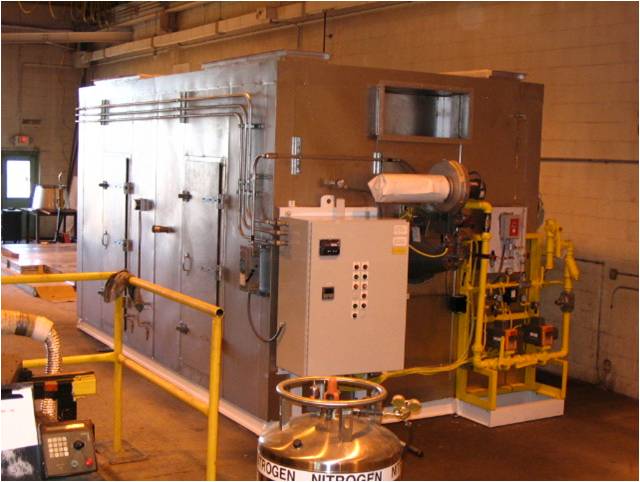
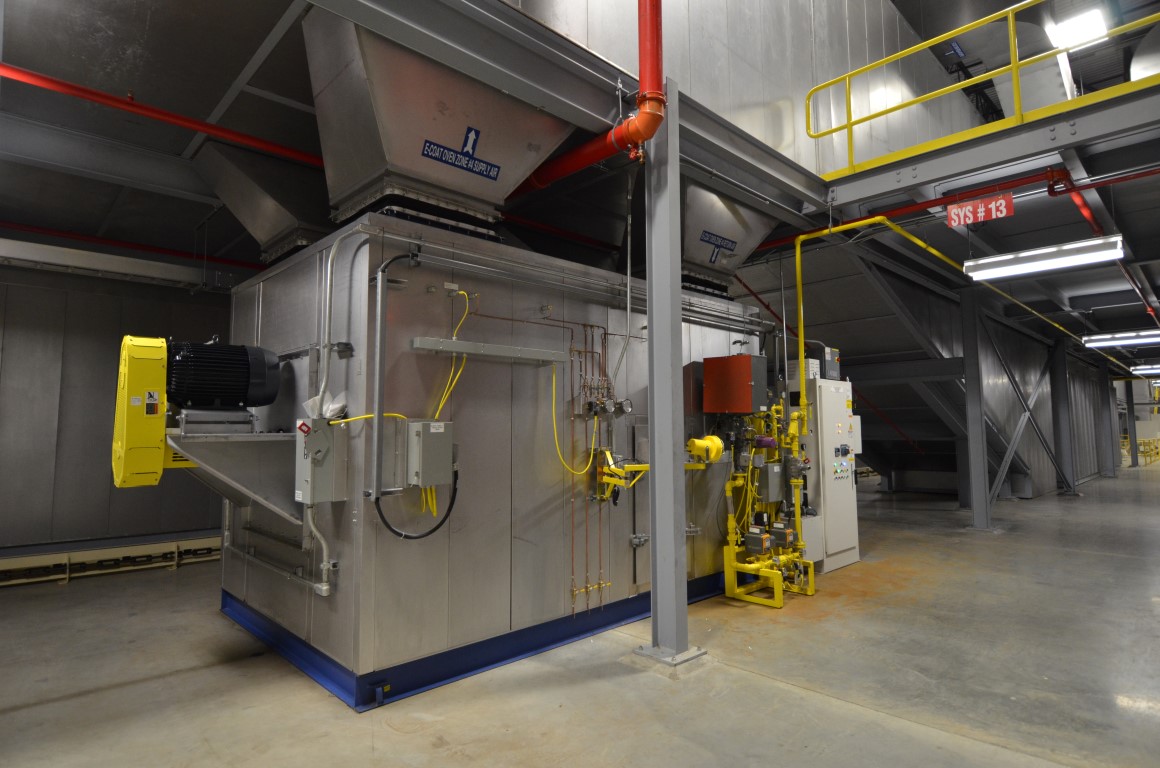
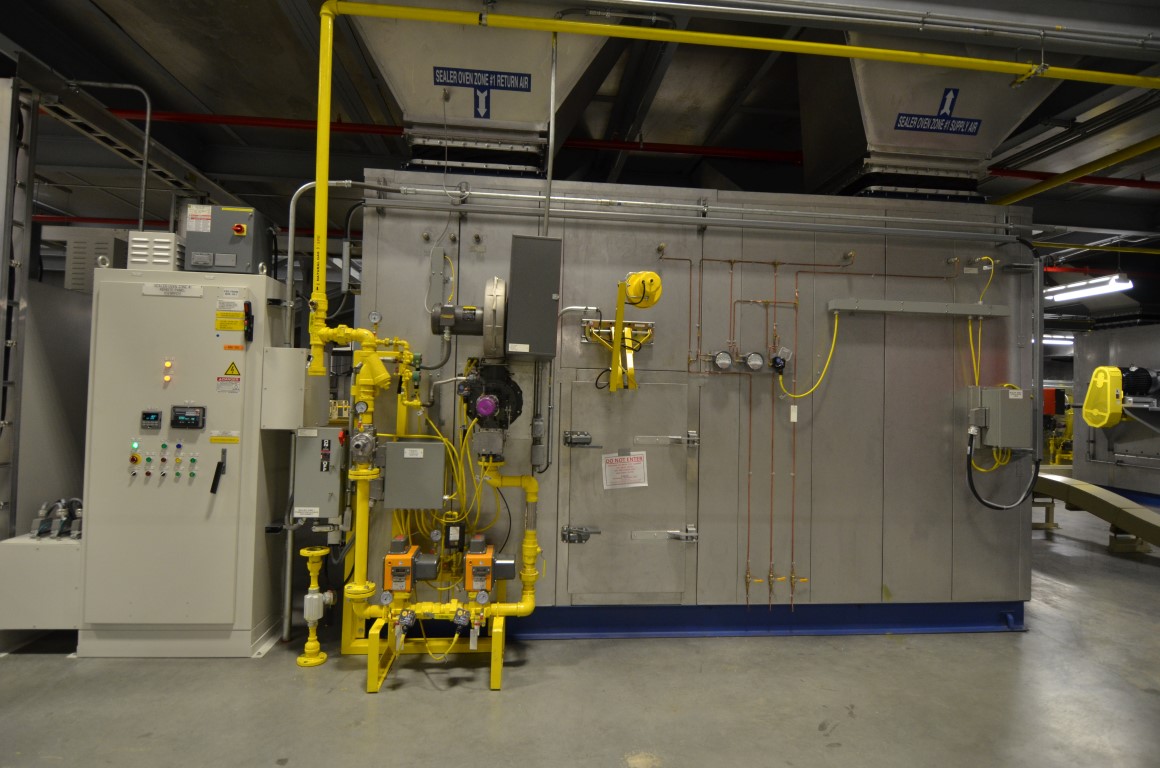
- The third key part of an industrial oven is the heating system: heater box, burner, ductwork, fan, and heat exchanger (HEX) - if applicable. Even within convection style ovens, there are several types of heating systems: direct-fired, indirect-fired, and semi-indirect fired.
- Direct-fired ovens do not use a heat exchanger, the hot, burner-fired air is sent directly into the oven, along with the products of combustion. For white paints, this can cause a yellowing of the paint color, so direct-fired ovens are only used for under layer coats such as Electro-coat (electro-deposition), sealer, and primer. It can also be used on Electrophoretic or black E-Coat paints for truck frames or service parts. Direct-fired ovens are not used for top coats, base coat, or clear coat.
- Indirect-fired ovens utilize an air-to-air heat exchanger (HEX), using the hot combusted air to heat fresh, clean air. The "clean" hot air is then sent into the oven itself. This way, the hot air in the oven is free from products of combustion and the white-painted parts will not yellow. Indirect-fired ovens are considered safer because there isn't a risk that gas will leak into the oven, and recirculated VOC-laden air from the oven will not reach the open flame of the burner. Typically, indirect-fired ovens do not require explosion relief.
- Semi-indirect ovens (or semi-direct ovens) are less common, but are sometimes utilized for safety. In the semi-indirect oven, the burner is offset in its own firing chamber, with a combustion blower providing fresh air. There is no heat exchanger, the combustion blower pushes the hot, fired air into the oven's recirculation ductwork, and it's carried down into the oven. In this design, products of combustion still reach the oven, since there is no heat exchanger, but the solvents or VOCs that flash off in the oven will never reach the burner, as they would in a direct-fired oven.
- The last critical element not touched on above is the conveyor which moves the vehicles or parts through the oven. Typically a chain-type conveyor is used here due to the heat load. New TKS oven designs locate the conveyor drive motor outside the oven, and only the chain portion inside. The chain and carrier may also be shrouded or covered by a metal sheathe with only the jig and parts sticking out. This reduces heat load on the oven, reduces dirt and grease inside the oven, and extends the lift of the conveyor itself.
Learn more about the entire Paint System See completed Industrial Oven Projects
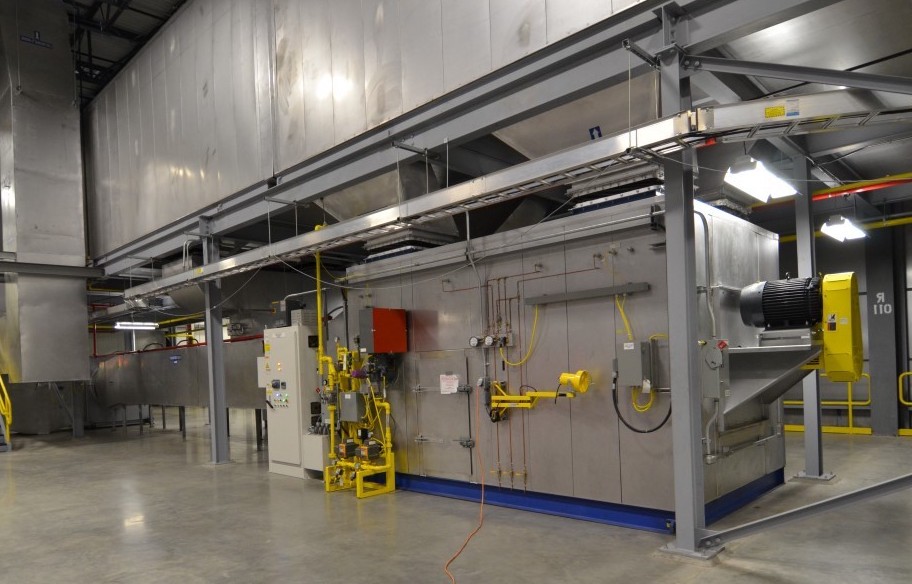




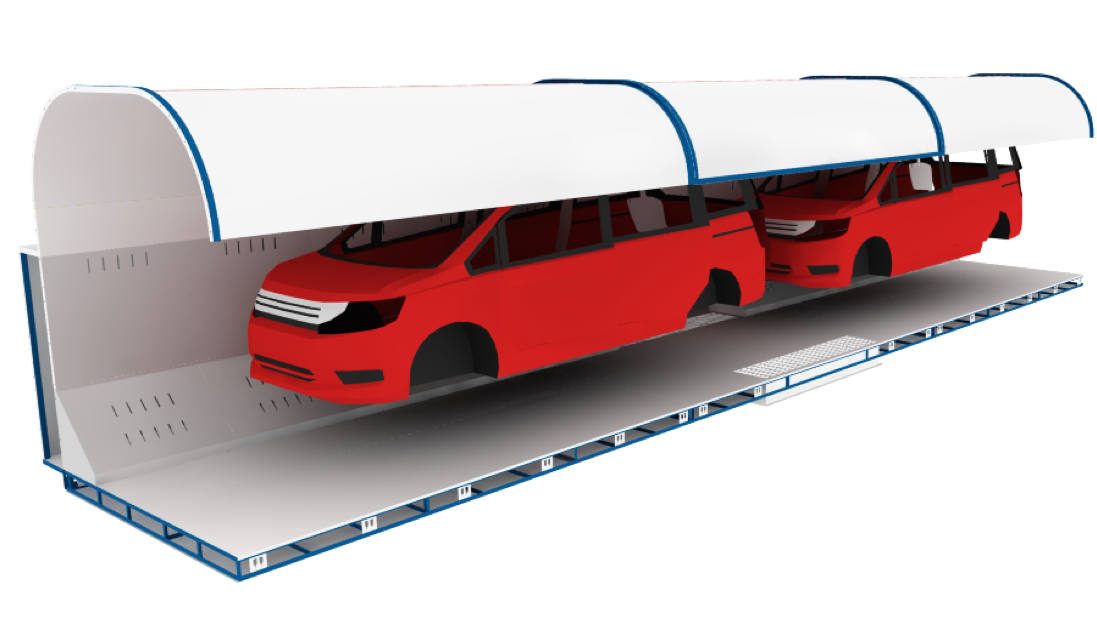


Paint Cure Oven Types
TKS' most common type of industrial oven is a paint oven for curing coatings on vehicles, parts, or other components. Our paint ovens typically have a continuous conveyor running through, and have been used in several different industries, including: Automotive, Aerospace, Heavy Trucks, Motorcycle, ATVs/UTVs, Parts suppliers, and other vehicle-related manufacturing industries.
There are several different varieties of industrial paint oven:
- E-coat Oven: The first oven in a paint shop is the E-Coat Oven. Also known as the ED, PTED, or ELPO oven. After the Electro-coat is applied by submerging the parts in the E-coat tank, the parts are rinsed and sent through the E-coat bake oven to dry and cure. The E-coat oven is the hottest oven in the paint shop at temperatures of ~350°F. The Electrocoat paint is held at temperature for 20 minutes where it cross-links and hardens. E-Coat is a water-based paint, so there's very low amounts of VOC in the E-coat oven, but it does tend to create smoke at high temperatures when the E-Coat drips off onto the hot oven surface. Oven air turnover and exhaust is required to keep temps up and smoke down. An air pollution abatement system like a Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) may be needed to control the amount of smoke.
- Sealer Oven: The second type of oven is the Sealer Oven which is the only paint oven that does not cure a paint coating layer. Instead, the sealer oven is used to dry and cure the polymer-based sealer applied to the seams of the vehicle to make it water-tight.
- Primer Oven: The primer oven is used to cure the primer layer of paint, which coating be liquid sprayed or powder coat primer. The primer oven is optional and is not used in a 3-wet paint process where the primer, basecoat, and clearcoat layers are applied after sealer oven and then cured together.
- Drying Oven: The dry-off oven is optional often not used. It is only used when the primer coat is wet sanded, rinsed, and dried before applying the base and clear topcoats.
- Heated Flash Off (HFO): Heated Flash-off tunnels or HFOs are essentially small ovens that only heat up to 160-180°F to dehydrate the outer layer of waterborne paint layer before applying the next liquid spray layer. The HFO is not needed for a solvent-borne paint, instead an ambient temperature flash off tunnel may be used. Two HFOs are used in a 3-wet paint booth process, between prime and base coat booths, and between base and clear coat spray booths.
- Top Coat Oven: The final and most important oven, it finishes the final paint cure, determining the finish quality that all customers will see. If there's no primer oven, as in a 3-wet process, then the Top Coat oven is responsible for fully drying and curing all three layers of primer, base coat, and clear coat. The topcoat oven is almost always an indirect-fired oven with heat exchanger to preserve the color integrity of the base coat and color coat layers.
TKS manufacturers industrial ovens for large-scale manufacturing applications like Automotive and Aerospace. TKS builds batch ovens, drying ovens, industrial ovens, paint ovens, cure ovens, and more.
Other Types of Industrial Ovens
- Cure Oven: typically used for parts curing. The material can be a composite like carbon fiber, a ceramic, a powder, or plastic resin. During the curing process, the part or coating will harden. Also called a heat-treatment oven.
- Drying Oven: drying ovens or dry-off ovens are used to remove moisture from the surface of an object. Drying ovens typically operate at a lower temperature, around 180-220°F. Can be used to remove water-based liquids or solvent-based liquids. Dry-off ovens are often used after a vehicle (or parts) wash/rinse cycle, when they need to be dried fully before the painting or coating process.
- Baking Oven: A baking oven typically combines the dry-off and cure functions, where the items to be baked are first dehydrated or the solvent flashes off, and then a chemical reaction takes place (polymer cross-linking, etc). Baking ovens are also used for food production and cooking or roasting.
- Infrared (IR) or Radiant Oven: This type of oven uses radiant heat energy to heat up the air and the parts inside the oven. Contrary to a convection oven, it may not use any air circulation. This helps reduce the amount of dirt and debris that may get stirred up and land on the vehicle or part. The first zone(s) or heat-up zones of a continuous oven are often IR or radiant zones to help reduce the amount of dirt that hits the paint while the outer layer is still wet.
- Batch Oven: A batch oven is a small oven that heats up and cools down in discrete phases. The parts or items to be heated are wheeled in on an oven cart, the door is shut and the oven is turned on. The parts heat up and are held at temperature inside the batch oven for the specified time, say 20 minutes, then the oven is turned off, opened up and allowed to cool. Once cooled, the parts may be rolled out and the process starts again. Batch ovens are used for low production rate processes. The batch oven is in direct contract to the continuous oven.
- Continuous Oven: parts, vehicles, food, equipment, whatever is being heated, is transported through the oven on a conveyor. This entering and exiting of the oven happens continuously as the oven stay at temperature in each zone. As the parts are transported through the oven, they heat up, hold, and cool down in the same heating phases of the batch oven. The continuous oven is used for high production rates. The oven may be made as long as is necessary to support the conveyor speed and the desired production rate.
- Post-Oven Cooling Tunnel: Depending on the production rate, after the exit of each oven, there may be a cooling tunnel which blows cold air to cool the parts and/or bodies before their next process step. The cooling tunnel is optional depending on plant layout and production rate. Most process steps that involve a human/manual process or involve paint application will have a minimum temperature of ~50°C or ~120°F for worker safety and for ideal paint appearance. If the parts don't have enough time to cool down to those temperature via ambient air temperatures, then a cooling tunnel is used.
Fuel source: Most ovens are gas-fired, but there are some electric heater driven ovens. Typically gas-fired ovens are much cheaper to operate, so electric ovens are only used where natural gas is not available and propane is too expensive or not readily available.



Paint Shop Layout with Ovens Highlighted:
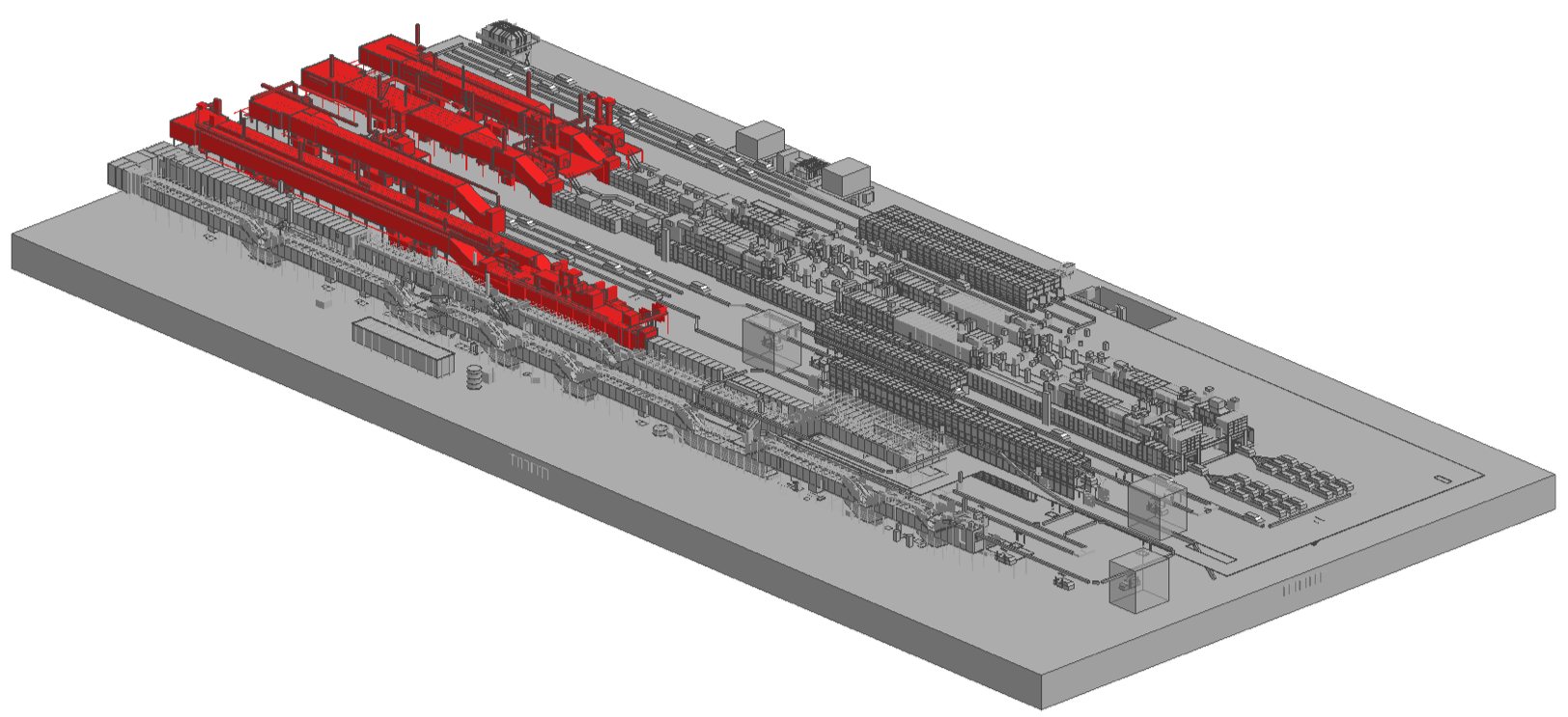

Industrial Oven Installations & Customers:
Currently in use at:
- Honda (8)
- Toyota (11)
- Nissan (8)
- Kia (2)
- Others: Subaru, Mazda, Mitsubishi, Harley Davidson, The Boeing Company, Chiyoda, Heartland, TOA, and more.
TKS manufacturers industrial ovens for large-scale manufacturing applications like Automotive and Aerospace. TKS builds batch ovens, drying ovens, industrial ovens, paint ovens, cure ovens, and more.
Need a quote?
TKS Offers
Worldwide Installation and Service

Turn-key Equipment Installation
Let TKS handle every aspect of your industrial oven project from start-to-finish. Give us a call today at 248-786-5000.
Annual Oven
Balance Assessments
TKS offers monthly, quarterly, and yearly oven health check assessments to evaluate cure performance, oven balance, heat loss, and perform critical preventative maintenance tasks. Let the industrial oven experts handle the maintenance for you.

Purchase New Systems
Ready to purchase a new bake oven, cure oven, paint oven or complete paint system? We're here to help with quick turnaround times.

Troubleshoot Equipment
Having a problem with your industrial oven? Our oven experts and engineers are always available to help. We can service all manufacturer's make and model oven.

Pay-by-the-day consulting services
Need an engineer to come to your plant location to help for the day? No problem. Our engineers are available to help out for a minimal daily fee.
Access to TKS Engineering Team
If you need help, advice, or expertise, the TKS Engineering team is always available to assist our customers.